Chemistry Lab Equipment
| Beaker - A beaker is a glass container with a flat bottom and a small spout for pouring. It is used in the chemistry lab for mixing, heating, and stirring liquids. Beakers come in various sizes and are shaped like a cylinder. |  Beakers Beakers |
| Bunsen burner - The Bunsen burner is a metal tube that produces a flame from gas such as methane, propane, or butane. It is used in the lab for heating and sterilizing. The Bunsen burner is named after German chemist Robert Bunsen. |  Bunsen burner |
Crucible - Crucibles are containers used for heating substances to very high temperatures. They are generally made from materials such as porcelain, nickel, and alumina.
| Erlenmeyer flask - This is a type of chemistry flask with a conical shaped body, a cylindrically shaped neck, and a flat bottom. It generally has measurement marks on the side. It is similar to a beaker, but has the cone shaped body. The cone shape reduces losses from evaporation and helps to prevent spills when stirring the liquid. |  Erlenmeyer flask |
| Funnel - A funnel is a pipe with a wide mouth that helps to pour substances into a container without spilling. In a chemistry lab, funnels are often used together with filters to separate a mixture. | 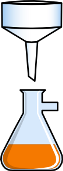 Funnel and flask |
| Gloves - Laboratory gloves are important to wear in order to protect the skin from chemical substances. Always listen to your teacher and make sure to wear gloves when performing experiments. |  Always wear gloves |
| Goggles - Goggles are very important when performing experiments of any kind. They can keep dangerous chemicals and other substances from damaging your eyes. Always wear your goggles in the lab! |  Always wear goggles |
| Graduated cylinder - A tall skinny cylinder used to measure volumes. It is generally a more accurate way to measure volume than a typical beaker or flask. |  Graduated cylinder |
| Mortar and pestle - A mortar and pestle are used to crush and grind solids into a powder. The mortar is a bowl and the pestle is a small club-shaped tool. They are typically made from ceramic or stone. |  Mortar and pestle |
| Pipette - A narrow glass tube used to transfer liquids from one place to another. Pipettes sometimes are used for measurement. The accuracy of different pipettes varies widely. | Pipette |
Scoopula - A scoopula is a metal spatula-type utensil used to scoop up solids such as powders in a chemistry lab.
Stirring rod - A skinny solid glass rod used in chemistry to mix chemicals and liquids. A stirring rod is typically about the length of a long straw and has rounded ends.
| Test tube - A test tube is a glass or plastic tube used for holding, mixing, and heating small quantities of liquid chemicals. Test tubes often have a flared top to help with pouring. They come in a variety of sizes. Test tube holder - A stand built for holding multiple test tubes. Test tube brush - A brush designed to help clean out test tubes. Test tube clamps - Clamps that hold test tubes while using them to heat up chemicals during a lab experiment. | 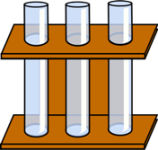 Test tubes in a holder |
Thermometer - A device used for measuring the temperature of a substance.
Triangle - A triangle made of clay pipes and wire that can withstand high temperatures. It is often used to hold a crucible.
Wire gauze - A wire gauze is used to support a beaker or flask when heating. The wire gauze helps to spread the heat evenly.