Solutions and Dissolving
What is a solution? A solution is a specific type of mixture where one substance is dissolved into another. A solution is the same, or uniform, throughout which makes it a homogeneous mixture . Go here to learn more about mixtures.
A solution has certain characteristics:
- It is uniform, or homogeneous, throughout the mixture
- It is stable and doesn't change over time or settle
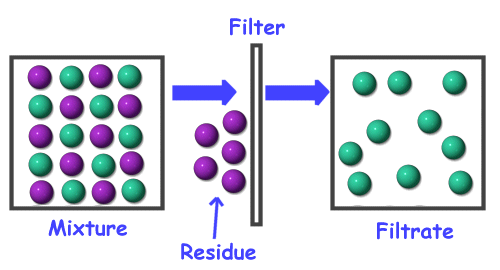
- The solute particles are so small they cannot be separated by filtering
- The solute and solvent molecules cannot be distinguished by the naked eye
- It does not scatter a beam of light
One example of a solution is salt water which is a mixture of water and salt. You cannot see the salt and the salt and water will stay a solution if left alone.
Parts of a Solution
- Solute - The solute is the substance that is being dissolved by another substance. In the example above, the salt is the solute.
- Solvent - The solvent is the substance that dissolves the other substance. In the example above, the water is the solvent.
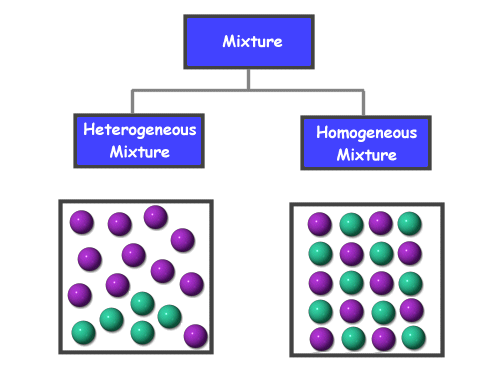
A solution is a type of homogeneous mixture
Dissolving
A solution is made when one substance called the solute "dissolves" into another substance called the solvent. Dissolving is when the solute breaks up from a larger crystal of molecules into much smaller groups or individual molecules. This break up is caused by coming into contact with the solvent.
In the case of salt water, the water molecules break off salt molecules from the larger crystal lattice. They do this by pulling away the ions and then surrounding the salt molecules. Each salt molecule still exists. It is just now surrounded by water molecules instead of fixed to a crystal of salt.
Solubility
Solubility is a measure of how much solute can be dissolved into a liter of solvent. Think of the example of water and salt. If you keep pouring salt into water, at some point the water isn't going to be able to dissolve the salt.
Saturated
When a solution reaches the point where it cannot dissolve any more solute it is considered "saturated." If a saturated solution loses some solvent, then solid crystals of the solute will start to form. This is what happens when water evaporates and salt crystals begin to form.
Concentration
The concentration of a solution is the proportion of the solute to solvent. If there is a lot of solute in a solution, then it is "concentrated". If there is a low amount of solute, then the solution is said to be "diluted."
Miscible and immiscible
When two liquids can be mixed to form a solution they are called "miscible." If two liquids cannot be mixed to form a solution they are called "immiscible." An example of miscible liquids is alcohol and water. An example of immiscible liquids is oil and water. Have you ever heard the saying "oil and water don't mix"? This is because they are immiscible.
Interesting Facts about Solutions
- There is a solvent called aqua regia which can dissolve the noble metals including gold and platinum.
- You can't see a beam of light when shining it through a true solution. This means fog is not a solution. It is a colloid.
- Solutions can be liquid, solid, or gas. An example of a solid solution is steel.
- Solids are generally more soluble at higher temperatures.
- Carbonated beverages are made by dissolving carbon dioxide gas into liquid at high pressure.